🔗 Latest Deployment: https://utfs.io/f/6c1dbbff-3665-4926-8862-ee1ef0181e0e-k73rem.zip
sdk-design-question
To install dependencies:
curl -fsSL https://bun.sh/install | bash
bun install
To run:
bun run src/index.ts
task
i want you to design a "better" state machine library, ideally i want it to use discriminated unions, and a clean simple zustand like api
State Machine Diagram:
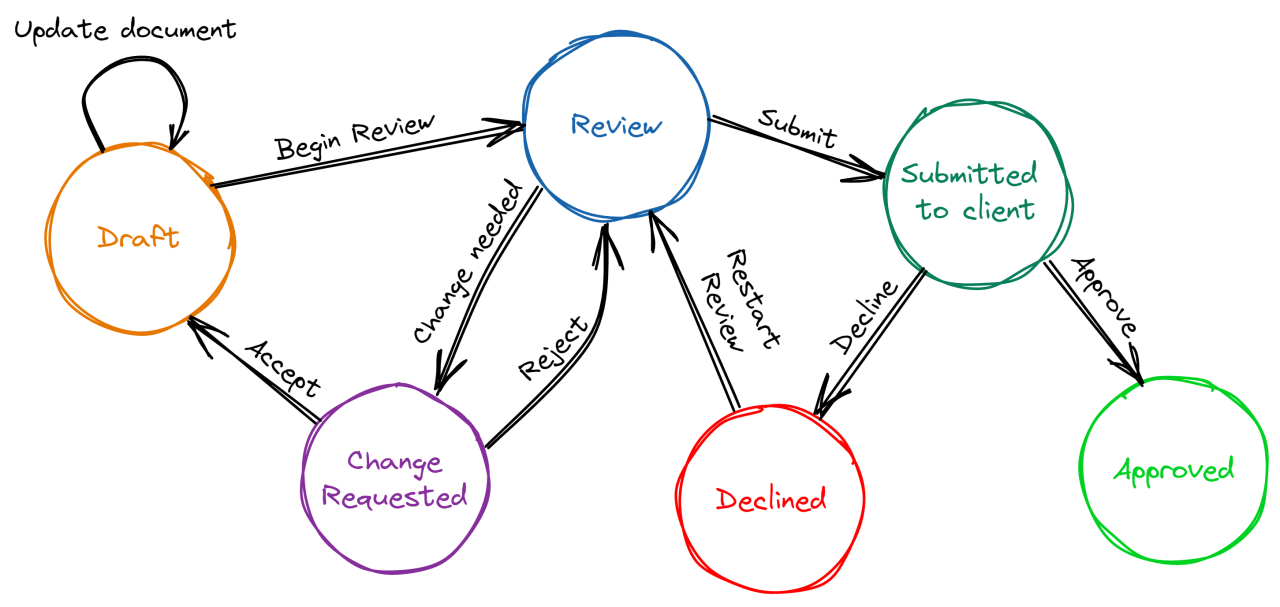
it should be type safe, it should have state, transitions and action definitions. this means i want these "CONTRACTS" explicitly defined in the type system
the seeded code is in src/ from zustand feel free to throw it out if you'd prefer, but would use it as a start on how to build this type of tool - you can choose another api if find that better
it should be usable like this
const useWebsocketStore = () => {
// YOUR SDK used here
// define state.kind (types of the state of the state machine explicitly)
// define state transitions explicitly (which states can go to which other states)
// define actions how the state has a transition to another state explicitly
// these are the contracts of the state machine
return { state, actions };
};
const App = () => {
const { state, actions } = useWebsocketStore();
switch (state.kind) {
case "idle": {
return <button onClick={() => actions.connect(state)}>Connect</button>;
}
case "connecting": {
return <p>Connecting...</p>;
}
case "connected": {
return (
<button onClick={() => actions.disconnect(state)}>Disconnect</button>
);
}
case "error": {
return <p>Something went wrong: {state.errorMessage}</p>;
}
}
};
use test/sdk.tsx to design the api
to submit, reply to the email you got with the zipped folder after an hr (max 75 mins) after you start
references
- zustand, also have an
example_zustand.tsxfile inside docs you can look at// Basic Zustand example import { create } from 'zustand' // Define your store const useStore = create((set) => ({ // State count: 0, // Actions increment: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count + 1 })), decrement: () => set((state) => ({ count: state.count - 1 })), reset: () => set({ count: 0 }), })) // Use in a component function Counter() { const { count, increment, decrement, reset } = useStore() return ( <div> <h1>{count}</h1> <button onClick={increment}>Increment</button> <button onClick={decrement}>Decrement</button> <button onClick={reset}>Reset</button> </div> ) } - discriminated unions
// Basic TypeScript discriminated union example
type NetworkState =
| { status: 'disconnected' }
| { status: 'connecting' }
| { status: 'connected' }
| { status: 'error'; errorMessage: string };
// Using the discriminated union
function handleNetworkState(state: NetworkState) {
// The 'status' property acts as the discriminant
switch (state.status) {
case 'disconnected':
return 'Ready to connect';
case 'connecting':
return 'Establishing connection...';
case 'connected':
return 'Connection established';
case 'error':
// TypeScript knows 'errorMessage' exists only in this case
return `Error: ${state.errorMessage}`;
}
}